 Business process optimisation (BPO) is a strategic approach to analysing, redesigning, and improving an organisation’s workflows. This method aims to boost efficiency, cut costs, and align operations with business objectives. BPO goes beyond minor tweaks. It seeks transformative changes that deliver significant value to customers, empower employees, and enable faster, more adaptive decision-making.
Business process optimisation (BPO) is a strategic approach to analysing, redesigning, and improving an organisation’s workflows. This method aims to boost efficiency, cut costs, and align operations with business objectives. BPO goes beyond minor tweaks. It seeks transformative changes that deliver significant value to customers, empower employees, and enable faster, more adaptive decision-making.
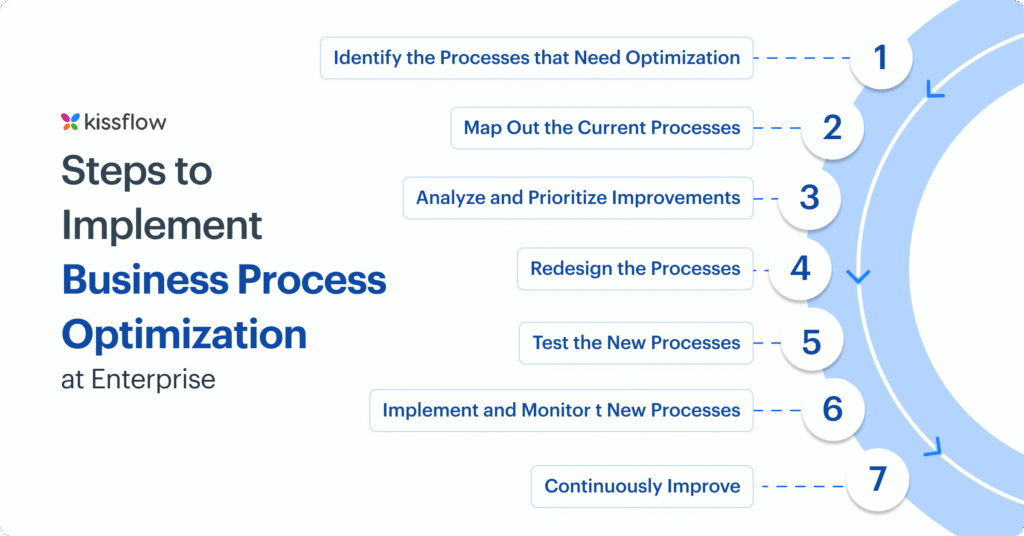
Business process optimisation involves several key steps. First, you analyse existing processes to understand how they currently function. Next, you identify inefficiencies, such as bottlenecks, redundant tasks, and unnecessary steps. Finally, you redesign these processes to make them more effective, often leveraging new technologies like automation and artificial intelligence (AI) to streamline tasks and boost productivity.
We’ll be discussing the methods, benefits and tools in this article to explain how business process optimisation works to improve an organisation’s operations.
Business Process Optimisation Methods
Organisations use various methods to optimise their processes. These approaches provide a structured way to identify and implement improvements:
Lean Management / Kaizen:
This method focuses on eliminating waste to shorten process cycle times, improve efficiency and increase value. The core principle of Lean is to identify and remove any activity that does not add value from the customer’s perspective. It emphasises creating a continuous flow of work and using a “pull” system, where work begins only when a customer requests it. Kaizen, a key part of Lean, promotes continuous, incremental improvements involving all employees, from the factory floor to top management.
Six Sigma:
This is a data-driven methodology that aims to reduce process variation and defects. It uses a structured approach, typically following the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control) model. Six Sigma seeks to achieve near-perfect results by identifying the root causes of problems and implementing solutions to ensure consistency and quality.
PDCA (Plan–Do–Check–Act):
This is an iterative, four-step management method for continuously improving business processes and products. In the Plan stage, define your objective and plan the changes needed to achieve it. Next, Do the planned changes on a small scale or in a controlled environment. The Check phase involves analysing the results and comparing them against the expected outcomes. Finally, Act on the findings: if the change was successful, implement it on a larger scale; if not, refine the plan and restart the cycle.
Process Mapping & Value-Stream Mapping:
Both of these are powerful visualisation techniques that help you improve business processes. Process mapping, or flow charting, represents each step in a workflow, from start to finish. This creates a clear picture of how workflows work, making it easy to spot bottlenecks, redundant tasks, and areas of unnecessary waiting. Value-stream mapping takes this a step further by showing the flow of materials and information required to deliver a product or service to a customer.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
This is a comprehensive management philosophy that focuses on long-term success by consistently meeting and exceeding customer satisfaction. This approach goes beyond simply inspecting finished products; it embeds a culture of continuous improvement throughout the entire organisation. TQM involves every employee, from front-line staff to top executives, in identifying and resolving issues to enhance the quality of processes, products, and services.
Tools: Choosing the Right Categories, Not Silver Bullets
Your selection of BPO stacks should be guided by a tool’s specific function, how well it integrates with your existing systems, the vendor’s plans for AI and process intelligence, and your organisation’s capacity to manage the platform.
- Discovery & Intelligence: Tools like Celonis and UiPath Process Mining are essential for the discovery phase. They use process mining to analyse your system logs, creating a factual, data-driven map of your processes. This helps you understand exactly how work flows in your organisation, providing a solid foundation for analysis.
- Modelling & Transformation: For redesigning processes, you need tools like SAP Signavio (Process Manager) or Bizagi. These platforms help you standardise and design future-state processes by providing a collaborative environment for mapping, documenting, and simulating new workflows.
- Automation & Orchestration: To execute your redesigned processes, you’ll need automation and orchestration platforms. Tools such as UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Appian provide capabilities like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for automating repetitive tasks, as well as workflow and case management to orchestrate the flow of work across different systems and teams.
- Analytics & BI: Once a process is implemented, Power BI or Tableau help you continuously measure its performance. These tools provide the analytics and business intelligence to report on outcomes. They track key performance indicators (KPIs) and hold teams accountable for achieving performance goals.
Benefits of Business Process Optimisation
Optimising business processes provides numerous advantages that can significantly impact an organisation’s bottom line and competitive position.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: By eliminating bottlenecks and automating repetitive tasks, BPO allows employees to focus on more strategic work, increasing overall productivity.
- Reduced Costs: Streamlining workflows and eliminating waste lowers operational costs related to labour, materials, and overhead.
- Improved Quality and Customer Satisfaction: Optimised processes reduce errors and defects, leading to higher-quality products and services and, consequently, more satisfied customers.
- Enhanced Agility and Adaptability: A more efficient and streamlined organisation can respond more quickly to market changes and new opportunities.
- Better Decision-Making: Optimised processes provide clearer data and insights, enabling leaders to make more informed and strategic decisions.
Common pitfalls, and how to avoid them
Major failures in business process optimisation don’t just come from technology. They often result from skipping essential human and data work. You can avoid these common pitfalls by focusing on a holistic approach:
Poor Data Quality or Missing Logs 📊
Process mining is only as good as the event data that feeds it. A common mistake is assuming your existing logs are clean and complete. Inaccurate, incomplete, or missing data leads to flawed analysis and poor decisions, ultimately undermining your optimisation efforts. To avoid this, invest in data validation and governance from the start. You need to ensure your data is accurate and structured correctly before you begin analysis.
Ignoring Change Management 🤝
Roughly three in four large transformations struggle because leaders underinvest in the human element. Without proper communication, training, and stakeholder alignment, employees may resist new processes or fail to adopt new tools. Active change programs, strong executive sponsorship, and frontline involvement are non-negotiable for success. When you actively involve the people who will use the new process, you gain their buy-in and make the transition much smoother.
Optimising Local KPIs, Not End-to-End Outcomes 🎯
A frequent mistake is focusing on a single department’s performance at the expense of the entire organisation. When you optimise a local key performance indicator (KPI), you can inadvertently create bottlenecks or new problems for other teams. Local gains can create global pain. To avoid this, use end-to-end metrics that measure the entire process from start to finish. Run pilots and validate improvements in a controlled environment to ensure your changes benefit the entire workflow, not just one part of it.
Final Thoughts
Business Process Optimisation (BPO) isn’t a single, one-off project; it’s a fundamental operating principle for modern, resilient enterprises. For both technology and business leaders, the directive is clear: view your business processes as products. Invest in data-first discovery to truly understand how your workflows function, balancing the need for speed with effective governance. Most importantly, design improvements that free people to focus on creative, strategic work that machines cannot replicate. By adopting this mindset, BPO transforms from a simple efficiency checkbox into a powerful, strategic engine for sustainable growth.